One of the most important gases on the earth is CARBON DIOXIDE. We know that plants need it to perform the process of photosynthesis. We know that humans and animals breathe it out while exhaling. We know that it is present in the air and it helps Earth hold the energy it receives from the Sun. But what else? Why is it considered one of the most important gases? Let's find out in this lesson.
In this lesson we will learn:
Carbon dioxide is a colorless and non-flammable gas at normal temperature and pressure. It is a chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to one carbon atom. Its chemical formula is CO2.
Carbon dioxide exists in Earth's atmosphere as a gas. It is a colorless gas that is heavier than air, does not burn, and at low concentrations, has no odor. At high concentrations, it has a sharp, acidic smell.
Although much less abundant than nitrogen and oxygen in Earth's atmosphere, carbon dioxide is an important constituent of our planet's air. It exists in the Earth's atmosphere at a concentration of approximately 0.04 percent.
Apart from gas form, it also has a solid and a liquid form.
The solid form of carbon dioxide is called Dry ice. It gets this name because it does not melt into a liquid when heated; instead, it changes directly into a gas with a process known as sublimation. Dry ice is colorless, odorless, and non-flammable, and can lower the pH of a solution when dissolved in water, forming carbonic acid (H2CO3).
Liquid carbon dioxide is carbon dioxide gas that is highly compressed and cooled to a liquid form. Liquid CO2 cannot exist as a liquid at atmospheric pressure. It must be pressurized to remain as a liquid.
Atmospheric CO2 comes from multiple natural sources, including:
Human activities such as the burning of oil, coal, and gas, as well as deforestation, are the primary cause of the increased carbon dioxide concentrations in the atmosphere.
Carbon dioxide is essential for internal respiration in the human body. Internal respiration is a process, by which oxygen is transported to body tissues and carbon dioxide is carried away from them. Carbon dioxide is a guardian of the pH of the blood, which is essential for survival.
But you can also hear that CO2 is harmful. Is it?
CO2 is not poisonous; as a gas, CO2 itself will not hurt you. This is an important fact to remember, as carbon dioxide is a vital part of the environment. Carbon dioxide becomes a poisonous gas when there is too much of it in the air you breathe. Besides the effects that can have on the planet and the atmosphere, carbon dioxide poisoning can lead to central nervous system damage and respiratory deterioration in humans and other breathing creatures. These may include headaches, dizziness, restlessness, a tingling or pins or needles feeling, difficulty breathing, sweating, tiredness, increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, coma, asphyxia, and convulsions.
The temperature of the Earth depends on a balance between incoming energy from the Sun and the energy that bounces back into space. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas that works to trap heat close to Earth. It helps Earth hold the energy it receives from the Sun so it doesn't all escape back into space. If it weren't for carbon dioxide, Earth's ocean would be frozen solid. Some of this energy is re-emitted back to Earth, causing additional heating of the planet.
But, increases in atmospheric carbon dioxide are responsible for about two-thirds of the total energy imbalance that is causing Earth's temperature to rise and that's why Carbon dioxide is considered a contributor to global warming.
Humans use carbon dioxide in many different ways. Some of them are:
During photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) from the air and soil. Within the plant cell, the water is oxidized, meaning it loses electrons, while the carbon dioxide is reduced, meaning it gains electrons. This transforms the water into oxygen and the carbon dioxide into glucose.
Photosynthesis by plants and the absorption of CO2 from the atmosphere by ocean water helps to remove CO2 from the atmosphere and can help clean the air if the concentration of CO2 is too high.
The carbon cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of the Earth.
Carbon dioxide plays a key role in Earth's carbon cycle, the set of processes that cycle carbon in many forms throughout our environment.
Volcanic outgassing and wildfires are two significant natural sources of CO2 in Earth's atmosphere. Respiration, the process by which organisms liberate energy from food, emits carbon dioxide. When you exhale, it is carbon dioxide (amongst other gases) that you breathe out. Combustion, whether in the guise of wildfires, as a result of slash-and-burn agricultural practices, or in internal combustion engines, produces carbon dioxide.
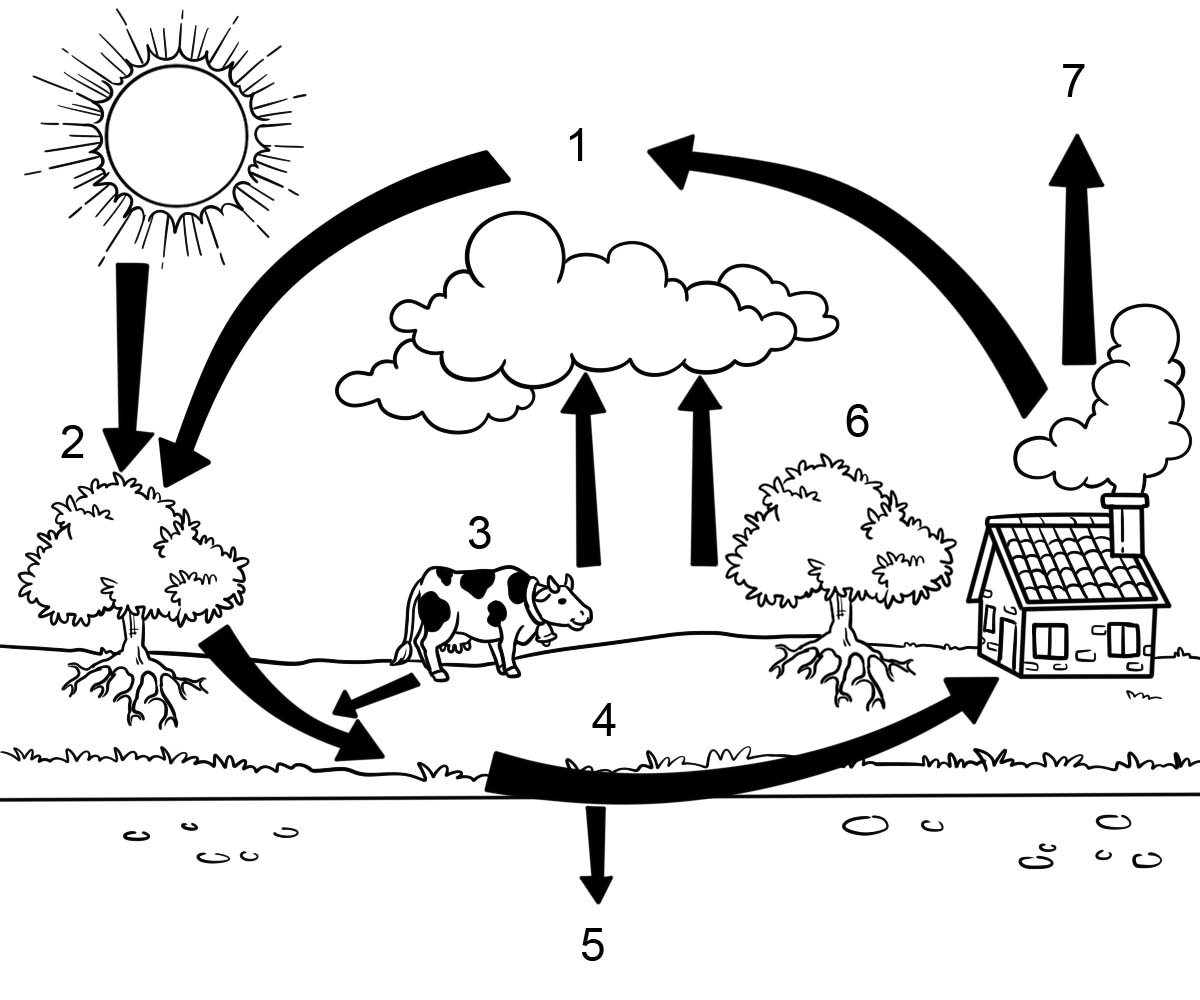
1. Carbon Dioxide
2. Synthesis light
3. Breathing Animals
4. Life, death, decay
5. Fossil fuels
6. Gas exchange of plant
7. The burning of fuel