Some of us can not imagine our life without eating sweets, like chocolate, candies, cookies... Or can not imagine drinks like tea or coffee without adding some sugar to sweeten them. Sugar is very present in our daily diet. When we say sugar, most of us first think of the very recognizable small white granules we add to our food, which we call "table sugar". But sugar is not just that substance. Sugar can be found in everything from fruits to candy.
What really sugar is, do we need in our diet, and is it healthy or not?
In this lesson, we are going to learn about SUGAR, and we are going to find out:
Chemically, sugar consists of carbon (C), oxygen (O), and hydrogen (H) atoms, and is classified as a carbohydrate. Carbohydrates are one of the three main nutrients found in foods and drinks. Sugar is simply the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates.
The following are the types of sugar:
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula C6H12O6. It is also called dextrose. It is found in fruits and honey and is the major free sugar circulating in the blood of higher animals.
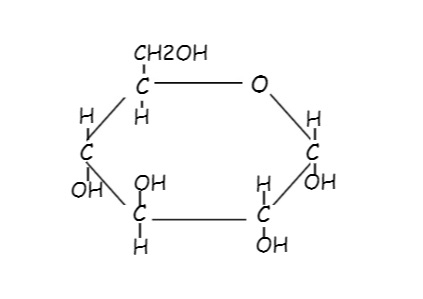
Chemical structure of Glucose
Fructose or fruit sugar is a simple sugar naturally occurring in fruit, honey, sucrose, and high fructose corn syrup. Its chemical formula is C6H12O6.
Galactose is a monosaccharide sugar that is about as sweet as glucose, and about 65% as sweet as sucrose. Its chemical formula is C6H12O6.
*Glucose, galactose, and fructose are common monosaccharides, the simplest form of sugar, and the most basic units of carbohydrates. They all have the same formula, C6H12O6, but different structures.
Sucrose is what we know as table sugar. Sucrose is made up of one molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose joined together. It is a disaccharide, a molecule composed of two monosaccharides: glucose and fructose. Sucrose is produced naturally in plants, from which table sugar is refined. Its formula is C12H22O11.
Lactose is a sugar found only in milk, that is why it is referred to as milk sugar. It is also present in dairy products and products made from milk, including cheese and ice cream. Lactose is a disaccharide. It is a sugar composed of galactose and glucose subunits. Its chemical formula is C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁.
Maltose is a sugar made out of two glucose molecules bound together. Maltose is also called malt sugar. It's created in seeds and other parts of plants as they break down their stored energy to sprout. Its chemical formula is C12H22O11.
*Sucrose, lactose, and maltose are common disaccharides, they are composed of two molecules of simple sugars linked to each other. They have the same chemical formula, C12H22O11, but different structures.
Longer chains of monosaccharides are not regarded as sugars and are called oligosaccharides or polysaccharides.
| Monosaccharides | Disaccharides |
| Glucose (dextrose) | Sucrose (table sugar) = glucose + fructose |
| Galactose | Lactose (milk sugar) = glucose + galactose |
| Fructose (fruit sugar) | Maltose (malt sugar) = glucose + glucose |
Now, as we know the types of sugar, we can discuss natural and refined sugars. Natural sugar is found in nature. It is present in fruit as fructose and in dairy products, such as milk and cheese, as lactose. Because these occur in nature, they are consumed in a minimally processed form. Foods with natural sugar have an important role in the diet because they provide essential nutrients that keep the body healthy and help prevent disease.
Refined sugar comes from sugar cane or sugar beets, which are processed to extract the sugar. It is typically found as sucrose. We use white and brown sugars. So, what's the difference between white sugar and brown sugar? White sugar is produced through a purifying process that removes a brown syrup called molasses. On the other hand, brown sugar either undergoes less processing to retain its molasses content or is produced by mixing white sugar with molasses.
Added sugars include sugars that are added during the processing of foods (such as sucrose or dextrose), foods packaged as sweeteners (such as table sugar), sugars from syrups and honey, and sugars from concentrated fruit or vegetable juices.
Sugar has many functions in food technology. The most important among these is that added sugar in foods acts as a:
Sugar’s most recognizable function. The sweetness perception of sugar depends on factors such as temperature, pH, concentration, the presence of other ingredients within finished products, and individual perceptions.
Sugar increases the osmotic pressure in a finished product and inhibits the growth of food spoilage bacteria.
Sugar crystal size can be chosen to add crunch and visual texture to the surface of finished products.
Fermentation is a critical process in baking and brewing. The yeast used in these processes uses sugar as a food source to produce ethanol, carbon dioxide, and water through the fermentation process. In bread-making, this speeds up the rising/leavening process. In alcoholic beverage production, fermentation delivers the target alcohol and sweetness level.
Sugar can enhance or depress certain flavor characteristics in your finished products.
Other uses of sugar are as a coloring agent, bulking agent, etc.