Water exists in three different forms: solid (ice), liquid (water), or gas (water vapor).
Evaporation and condensation are two processes through which water changes from one state to another. All matter is made of tiny moving particles called molecules. Evaporation and condensation happen when these molecules gain or lose energy in the form of heat.
For example, take water in a bowl and draw a line to indicate the level of water. Now, place this bowl of water in the sunlight. After some time, observe the level of water in the bowl. You will notice the water level is lowered. Where does the water from the bowl go? It has changed into vapor due to the heat of the sun. This is evaporation.
In a similar way, as water in a pot boils, the level of the water comes down. The water seems to disappear, but it actually moves into the air as a gas called water vapor.
Evaporation happens when a liquid is heated. The heat gives the liquid’s molecules more energy. This energy causes the molecules to move faster. If they gain enough energy, the molecules near the surface break away. These molecules escape the liquid and enter the air as a gas. Evaporation from plants is called transpiration.
In evaporation, water changes from a liquid to a gas.
Condensation is the opposite of evaporation. Think about when you pour ice cubes into a glass, what happens on its outer surface? Do you see small droplets of water appearing on the outer surface of glass? Water vapours present in the air, when touching the cold surface of the glass, get together to form droplets. This process is called condensation.
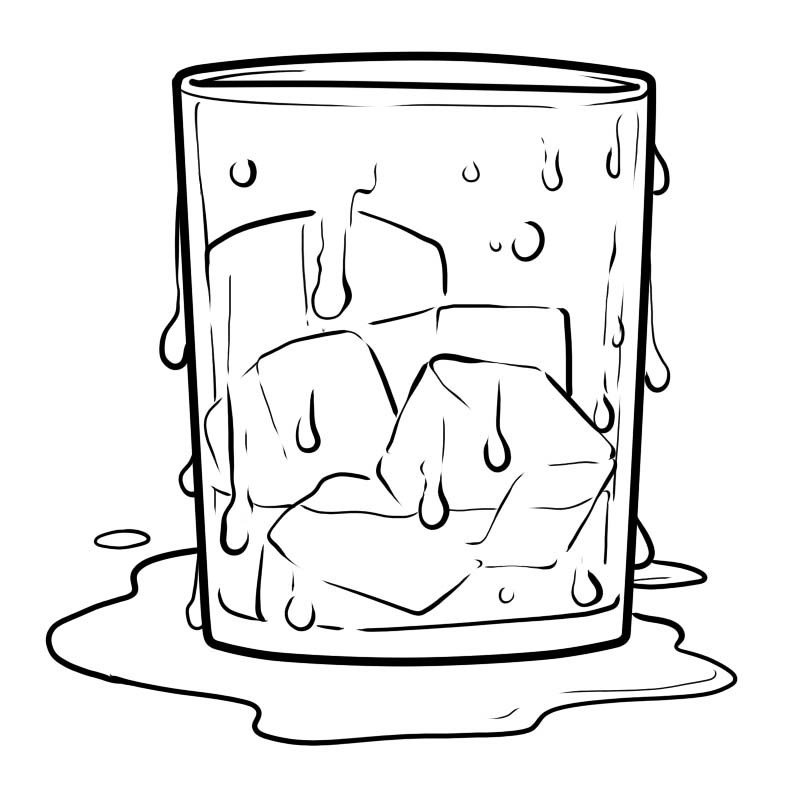

Condensation is caused by the loss of heat. Condensation happens when molecules in a gas cool down. As the molecules lose heat, they lose energy. As a result, they slow down. They move closer to other gas molecules. Finally, these molecules collect together to form a liquid.
In condensation, water changes from a gas to a liquid.
As the sun heats water in a pond, lake, river, or other water bodies, the water changes into water vapors and transfer to the atmosphere. This process is called evaporation. When water vapors reach the upper atmosphere they condense due to low temperature, form clouds, and fall back on earth in the form of rain, snow, and hail and sometimes in the form of dew and fog.
During winter when the morning temperature is very low, drops of water condense and suspended in the atmosphere as fog. The dew that forms on the grass overnight is another example of condensation. In intense cold days, these water droplets fall down as frost.
Water is constantly being recycled in the water cycle, through evaporation and condensation. This is the way nature distributes water throughout the land to support the life of plants, animals, and humans on earth.