An improper fraction has a top number larger than (or equal to) the bottom number.
Example:
 Where 3 is greater than 2
Where 3 is greater than 2
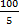 Where 100 is greater than 5
Where 100 is greater than 5
A fraction such as  has two numbers - Numerator and Denominator. For example, in
has two numbers - Numerator and Denominator. For example, in  7 is the numerator and 4 is the denominator. This means:
7 is the numerator and 4 is the denominator. This means:
- We have 7 parts.
- Each part is a quarter (1/4) of a whole.
Improper Fractions or Mixed Fractions
We can use either an improper fraction or a mixed fraction to show the same amount.
For example, 1 =
=  as shown here
as shown here

Converting improper fractions to mixed fractions
To convert an improper fraction to a mixed fraction, follow these steps:
- Divide the numerator to the denominator.
- Write down the whole number answer.
- Then write down any remainder above the denominator.
Example: Convert 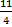 to a mixed fraction
to a mixed fraction
- Divide 11 by 4 i.e. 11 ÷ 4 = 2 with remainder 3.
- Write down the 2 and then write down the remainder (3) above the denominator (4).
- Answer: 2
 i.e. Quotient
i.e. Quotient 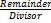
Convert mixed fractions to improper fractions
To convert a mixed fraction to an improper fraction, follow these steps:
- Multiply the whole number part by the fraction’s denominator
- Add that to the numerator
- Then write the result on top of the denominator
Example: Convert 3 to an improper fraction
to an improper fraction
- Multiply the whole number part by the denominator: 3 × 5 = 15
- Add that to the numerator: 15 + 2 = 17
- Then write that result above the denominator:
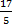
Adding and subtracting improper fractions
The rules for adding and subtracting improper fractions are the same as working with proper fractions.
Adding and subtracting improper fractions with common denominators
Step 1 – Keep the denominator the same.
Step 2 – Add or subtract the numerators.
Step 3 – If the answer is an improper form, reduce the fraction into a mixed number.
For example,  +
+  =
= 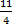
Thus, we have 2 
Adding and subtracting improper fractions with different denominators
- Find the Lowest Common Multiple (LCM) between the denominators.
- Multiply the numerator and denominator of each fraction by a number so that they have the LCM as their new denominator.
- Add or subtract the numerators and keep the denominator the same.
- If the answer is an improper form, reduce the fraction into a mixed number.
Example: Subtract the fraction  -
- 
- The Lowest Common Multiple between 6 and 8 is 24.
- Find a number that when multiplied to the top and bottom of 76
 , we get the LCM (24) as the new denominator:
, we get the LCM (24) as the new denominator: 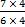 =
= 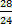
- Find a number that when multiplied to the top and bottom of 3/8, we get the LCM (24) as the new denominator: 3
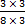 =
= 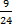
- Since our fractions now have equal-sized slices, we can subtract their numerators. Thus, we now have
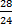 -
- 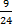 =
= 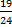 of a whole.
of a whole.
![]() Where 3 is greater than 2
Where 3 is greater than 2![]() Where 100 is greater than 5
Where 100 is greater than 5![]() has two numbers - Numerator and Denominator. For example, in
has two numbers - Numerator and Denominator. For example, in ![]() 7 is the numerator and 4 is the denominator. This means:
7 is the numerator and 4 is the denominator. This means:![]() =
= ![]() as shown here
as shown here
![]() to a mixed fraction
to a mixed fraction![]() to an improper fraction
to an improper fraction![]() +
+ ![]() =
= ![]()
![]()
![]() -
- ![]()