The periodic table of the chemical elements is a list of known elements. In the table, the elements are placed in the order of their atomic numbers starting with the lowest number. The atomic number of an element is the same as the number of protons in that particular atom.
Dmitri Mendeleev gets the credit for designing the modern periodic table.
Each element has a square in the periodic table. There are 3 pieces of information in each square
- the name of the element
- its official chemical symbol
- its atomic number
For example, the square for iron will look a bit like this:
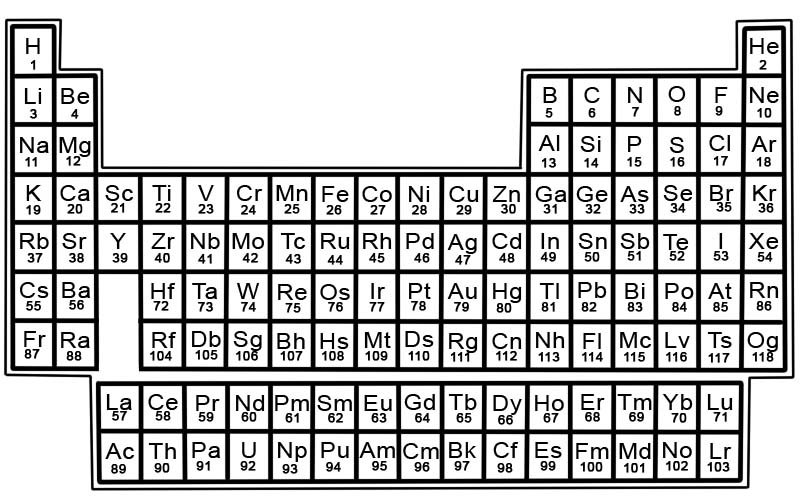
Elements in the periodic table are arranged in rows and columns.
- Rows are called periods. A period is a row of elements in the periodic table whose properties change gradually and predictably.
- Columns are called groups. The periodic table has 18 columns of elements. Each column contains a group, or family, of elements. A group contains elements that have similar physical or chemical properties.
Zones on the periodic table
The periodic table can be divided into sections.
One section consists of the first two groups, Group 1 and 2, and the elements in Groups 3-18. These are the representative elements. They include metals, metalloids, and nonmetals.
Metals
Examples: iron, tin, sodium, and plutonium.
- usually solid at room temperature (mercury is an exception)
- high luster (shiny)
- metallic appearance
- good conductors of heat and electricity
- malleable (can be bent and pounded into thin sheets)
- ductile (can be drawn into wire)
- corrode or oxidize in air and seawater
- usually dense (exceptions include lithium, potassium, and sodium)
- may have a very high melting point
- readily lose electrons
Metalloids
Examples: boron, silicon, and arsenic.
- dull or shiny
- usually conduct heat and electricity, though not as well as metals
- often make good semiconductors
- often exist in several forms
- often ductile
- often malleable
- may gain or lose electrons in reactions
Nonmetals
Examples: oxygen, chlorine, and argon.
- dull appearance
- usually brittle
- poor conductors of heat and electricity
- usually less dense, compared to metals
- usually low melting point of solids, compared with metals
- tend to gain electrons in chemical reactions
Groups 1 and 2
- Group 1 - Alkali metals. Examples: sodium, lithium, and potassium.
- Group 2 - Alkaline earth metals Examples: beryllium, magnesium, calcium, barium, and radium. Each alkaline earth metal is denser and harder and has a higher melting point than the alkali metal in the same period. Alkaline earth metals are reactive but not as reactive as alkali metals.
Groups 13 to 18
Group 13 – Boron family
- Examples: boron (B), aluminum (Al), gallium (Ga), indium (In), and thallium (Tl).
- They have three valence electrons.
Group 14 – Carbon family
- Examples: carbon (C), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), tin (Sn), and lead (Pb).
- They all have four valence electrons.
Group 15 – Nitrogen family
- Examples: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), and bismuth (Bi).
- These elements all have five valence electrons.
- Nitrogen and Phosphorous are non-metals.
Group 16 – Oxygen family
- Examples: oxygen (O), sulfur (S), selenium (Se), tellurium (Te), and radioactive polonium (Po).
- This group has six valence electrons
- These are also known as the chalcogens.
Group 17 – Halogens
- Examples: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and astatine (At).
- They have seven valence electrons.
- This group is the first one to consist of entirely non-metals.
- Halogens are highly reactive, and as such can be harmful or lethal to biological organisms in sufficient quantities.
- The symbol X is often used generically to refer to any halogen.
- The name “halogen” means “salt-producing”. When halogens react with metals they produce a wide range of salts, including calcium, fluoride, sodium chloride (table salt), silver bromide and potassium iodide.
Group 18 – Noble gases
- There are six noble gases – helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon.
- They are all gases and are found in the air. They make up around 0.96% of the atmosphere.
- All of them are monoatomic, meaning each molecule is a single atom.
- They almost never react with other elements. This is because they have a full 8 electrons outer electron shell.
- Noble gases have very low boiling and melting points, which make them useful as cryogenic refrigerants.
Transition metals
- The elements in Groups 3-12 are transition elements.
- They are all metals.
- Most transition elements are found combined with other elements in ores.
- A few transition elements such as gold and silver are found as pure elements.
- The filaments of light bulbs are made of tungsten (element 74) which has the highest melting point of any metal and will not melt when a current passes through it.
- Mercury, which has the lowest melting point of any metal, is used in thermometers and barometers.
- Mercury is the only metal that is a liquid at room temperatures.
Iron triad
Three elements in group 4 – iron, cobalt, and nickel – have such similar properties that they are known as the iron triad.
Platinum group
Ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, osmium, iridium, and platinum are sometimes called the platinum group because they have similar properties. They do not combine easily with other elements. As a result, they can be used as catalysts.
Inner transition elements
Some transition elements, called the inner transition elements, are placed below the main table. These elements are called the lanthanide and actinide series because one series follows the element lanthanum, element 57, and the other series follows actinium, element 89.
Lanthanides - The first series, from cerium to lutetium, is called the lanthanides. The lanthanides also are called the rare earth because at one time they were thought to be scarce. They are soft metals that can be cut with a knife.
Actinides – All the actinides are radioactive. Thorium, protactinium, and uranium are the only actinides that now are found naturally on Earth. All other actinides are synthetic elements. Synthetic elements are made in laboratories and nuclear reactors.
