Every cell requires to move materials in and out of the cell. Some of the materials that require to be transported in and out of cells include proteins, food, oxygen, water and carbon dioxide. There are two major types of transport in cells:
PASSIVE TRANSPORT
When small particles travel from areas of higher concentration to regions of lower concentration, it is referred to as passive transport. This is the normal flow of materials. There are two types of passive transport; osmosis and diffusion. Osmosis refers to the movement of water molecules from a region of high water concentration to a region of lower solvent concentration through a cell membrane. Diffusion on the other hand refers to the movement of particles from a region of high concentration to regions of lower concentration against a concentration gradient. This type of transport does not require energy or ATP.
Below are examples of this type of transport in cells:
ACTIVE TRANSPORT
When small particles travel from a lower concentration to a higher concentration, it is known as active transport. This is against the normal flow of materials. Active transport requires ATP and energy. In case large particles need to enter or leave the cell, they require special types of active transport known as exocytosis and endocytosis.
Endocytosis happens when a cell needs to bring in large particles. “endo” means in the cell.
Exocytosis on the other hand happens when a cell requires to take out large particles. Think of “exo” as expelling from the cell. This is the process through which Golgi moves proteins out of the cell.
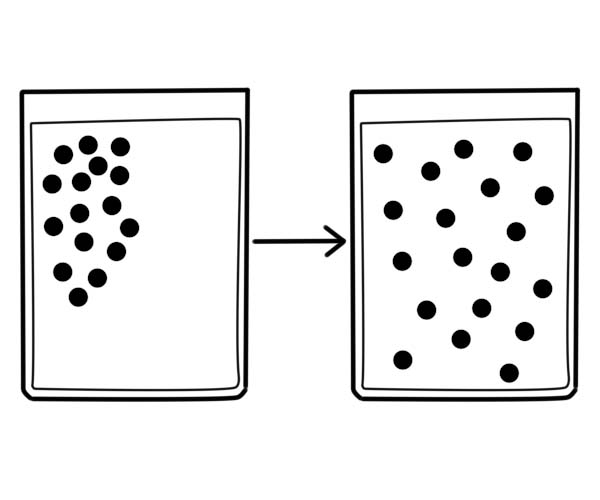
Diffusion
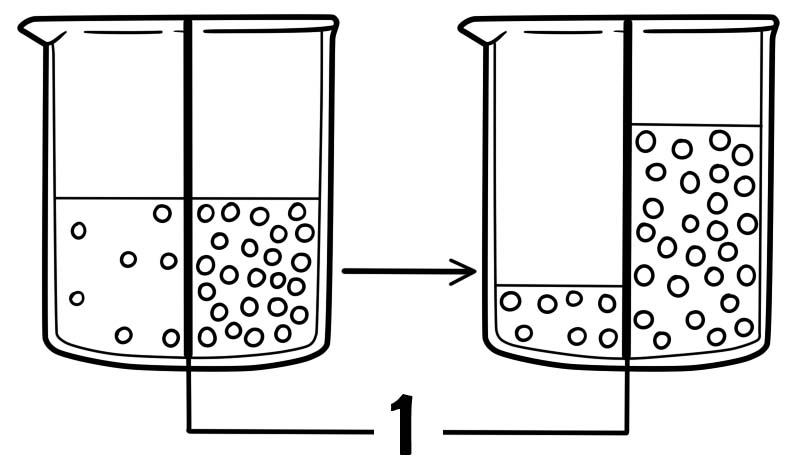
Osmosis
1. Semipermeable Membrane
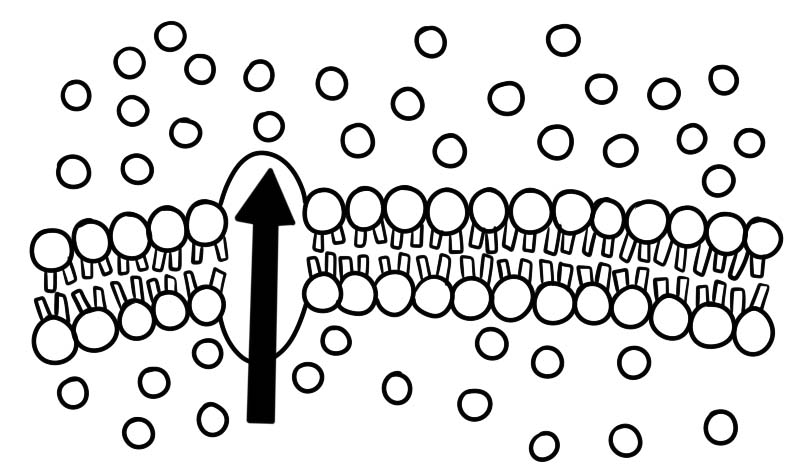
Active transport
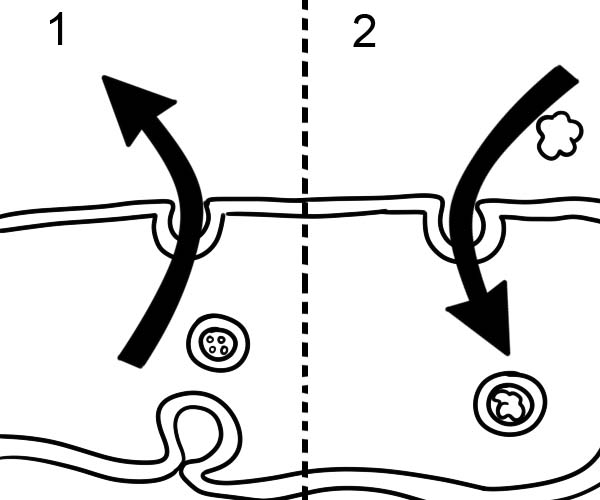
1. Exocytosis
2. Endocytosis