The urinary system is also referred to as the urinary tract or the renal system. This system is made up of the kidneys, urethra, bladder and ureters. The main purpose of this system is the elimination of wastes from the body. Other functions of this system include; regulation of blood pressure and blood volume, control of the levels of metabolites and electrolytes, and regulation of the pH of the blood. This system can be said to be the drainage system of the body that serves the purpose of eventual removal of urine.
There is an extensive supply of blood in the kidneys that comes through the renal arteries and leaves the kidneys through the renal vein. Every kidney is made up of functional units known as nephrons. Following blood filtration and processing, wastes (in urine form) leave the kidneys through the ureters. Ureters are tubes made up of smooth muscle fibers propelling urine towards the urinary bladder. Urine is stored in the bladder and then expelled from the body by a process known as urination or voiding. The urinary systems of males and females are very similar; they only differ in the urethra’s length.
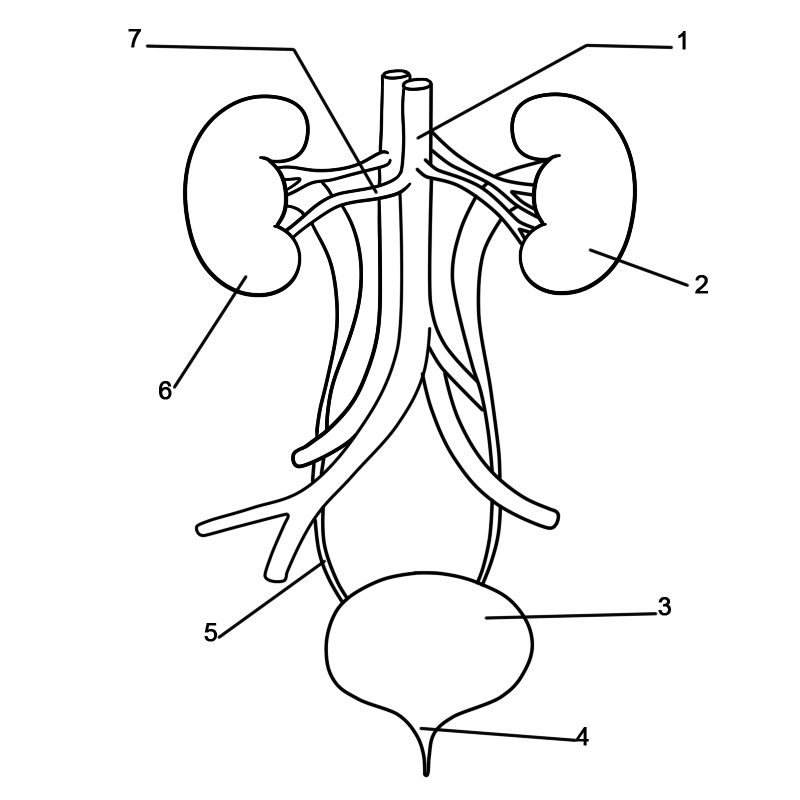
Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters into the bladder for storage. During urination, urine flows via the urethra in order to exit the body. The formation of urine takes place in the kidneys by blood filtration. Between 800 and 2,000 milliliters of urine are produced daily by healthy humans. This amount differs depending on the fluid intake as well as kidney function.
MICROANATOMY
If observed under a microscope, the urinary system is covered in a lining known as the urothelium. This is a type of a transitional epithelium. Contrary to the epithelial lining of many organs, transitional epithelium may flatten and distend. Urothelium covers most of this system including the bladder, renal pelvis and ureters.
FUNCTION
The major functions of the urinary system as well as its components include;
URINE FORMATION
The average production of urine in adult humans is 1 to 2 liters daily. This depends on the activity level, weight, environmental factors, state of hydration and the health of an individual. Polyuria is a condition of excessive production of urine that is more than 2.5 liters a day. Oliguria is a condition where less than 400 milliliters of urine are produced in a day while anuria is a condition where less than 100 milliliters of urine is produced per day.
The first step in the formation of urine is blood filtration in the kidneys. The kidney receives about 12 to 30% of cardiac output in a healthy human but this averages to about 20% or 1.25 liters per minute.
The nephron is the basic structural and functional unit of the kidney. Its main purpose is the regulation of the concentration of water and soluble substances such as sodium through filtering the blood, reabsorbing whatever is needed and excreting the rest in the form of urine. The regulation of the urinary system is done by the endocrine system by hormones like parathyroid hormone and aldosterone.