The human nose protrudes from the face. It has two nostrils and it is part of the respiratory system. The nose is also the major organ of the system known as olfactory system. The nasal bones, as well as the nasal cartilages, determine the shape of the nose. The nasal septum is the part that separates the nostrils and also divides the nasal cavity into two. The nose of a male is generally larger than that of a female.
The major purpose of the nose is respiration. The paranasal sinuses, the nasal cavity and the nasal mucosa lining conduct the required conditioning of the air that is inhaled by moistening and warming it. Nasal conchae, which are shell-like bones found in the walls of the cavities play a great role in this process. Nasal hair serves the purpose of filtering air, therefore, preventing large particles from getting into the lungs. Nasal hair is found in the nostrils. Sneezing is a reflex that expels unwanted particles that irritate the lining of the mucosa. Transmission of infections can be done by sneezing as aerosols are created in which these droplets can carry pathogens.
Another major purpose of the nose is olfaction. This refers to the sense of smell. In the upper nasal cavity lies the olfactory epithelium which contains specialized olfactory cells that are responsible for this function.
The nose is also involved in speech. Nasal consonants and nasal vowels are produced in a process known as nasalization. The nasal cavity is said to be the third most effective vocal resonator.
STRUCTURE
Several nasal cartilages and bones make up the bony and cartilaginous framework of the nose as well as the internal structure. The nose also contains soft tissues like the skin, nerves, muscles, epithelial, and mucous membrane. There are sebaceous glands in the skin and nasal glands are found in the mucous membrane.
The nose is made up of cartilage and bone. This provides strong protection to the internal structures of the nose. The cartilages are arranged in a way to allow flexibility in order to allow airflow.
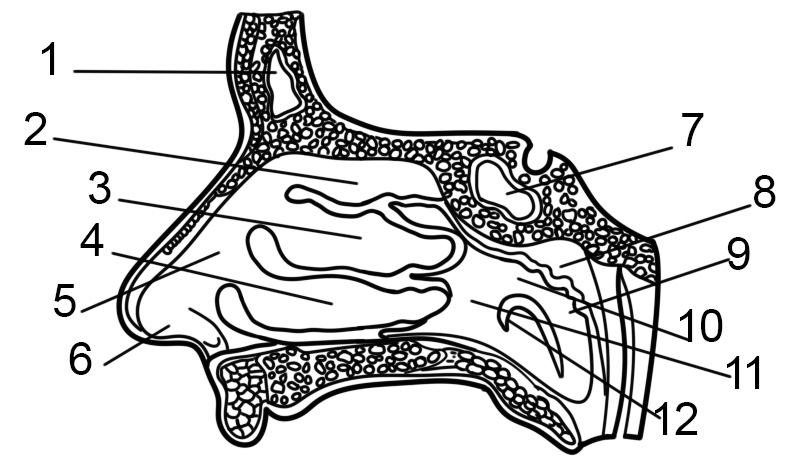
INTERNAL NOSE
CAVITIES
Nasal cavity refers to the large internal space of the nose. This cavity is divided into two cavities called fossae. They are divided by the nasal septum. Each fossa is a nostril continuation. The division of this cavity into two allows the functioning of the nasal cycle, slowing down the process of air conditioning.
CHOANAE
There exist two openings at the back of the nasal cavity, each opening from a fossa, they are known as choanae. Choanae are also known as posterior nostrils. They give entrance to the nasopharynx as well as the rest of the respiratory tract.
NASAL VALVES
These are also found in the cavity and their purpose is to provide resistance to airflow. This allows enough time for moistening and warming air.
NASAL VESTIBULE
This refers to the front-most part of the cavity. This part is enclosed by cartilages. The vestibule is lined with hair follicles, skin and many sebaceous glands.
LATERAL WALLS
On the lateral walls of every cavity are three conchae. They are arranged as superior, inferior nasal conchae and middle conchae.