The respiratory system is the system in the human body that enables us to breathe.
The act of breathing includes inhaling and exhaling air in the body; the absorption of oxygen from the air in order to produce energy; the discharge of carbon dioxide, which is the byproduct of the process.
Lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system which help in the exchange of gases.
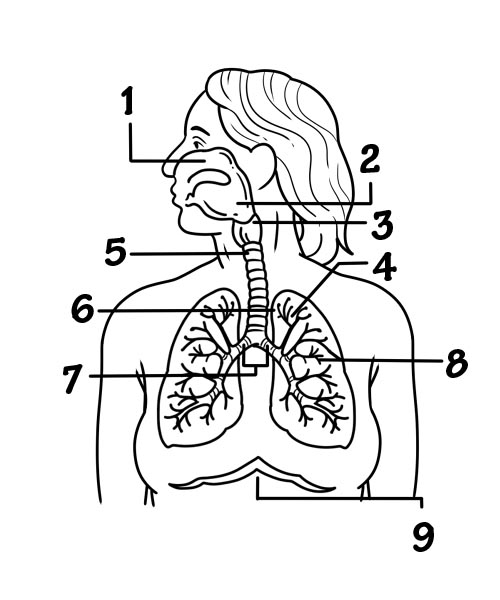
The respiratory tract in humans is made up of the following parts:
Taking air into the body through the nose and mouth is called inhalation.
Pushing air out of the body through the nose or mouth is called exhalation.
Air moves into and out of the lungs by the movement of muscles. The diaphragm and rib muscles contract and relax to move air into and out of the lungs. During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and moves downward. The rib muscles contract and cause the ribs to move outward. This causes the chest volume to increase. Because the chest volume is larger, the air pressure inside the lungs is lower than the air pressure outside. This difference in air pressures causes air to be sucked into the lungs. When the diaphragm and rib muscles relax, the air is pushed out of the lungs.
The walls of the alveoli are very thin and allow gases to enter into them. The alveoli are lined with capillaries. Oxygen moves from the alveoli to the blood in the capillaries that surround the alveoli. At the same time, carbon dioxide moves in the opposite direction, from capillary blood to the alveoli.
The process of getting oxygen into the body and releasing carbon dioxide is called respiration. There are actually two parts to respiration – external respiration and internal respiration.
The air inhaled through the nose moves through the pharynx, larynx, and trachea into the lungs. The air is exhaled back through the same pathway.
Inside the lungs, the oxygen then passes across the thin lining of the capillaries and into the blood. The oxygen binds to hemoglobin and is pumped through the bloodstream. The carbon dioxide from the blood diffuses into the alveoli and is expelled through exhalation.
The blood carries oxygen around the body. The oxygen is diffused through the capillary walls into the body tissues. The carbon dioxide also diffuses into the blood and is carried back to the lungs for release.
The oxygen that arrives at the cells from the lungs is used by the cells to help release the energy stored in molecules of sugar. Cellular respiration is the process of breaking down glucose to release energy. The waste products of cellular respiration include carbon dioxide and water. The carbon dioxide molecules move out of the cells and into the capillaries that surround the cells. As explained above, the carbon dioxide is removed from the body by the lungs.