Learning Objectives
In this lesson, students will
- Describe osmosis and osmotic pressure
- Describe solvent and solute
- Describe solution and different types of solution
- Understand the effect of osmosis in plant cells
- Understand the effect of osmosis in animal cells
What is osmosis?
Osmosis is the movement of water from a high concentration to a low concentration through a semi-permeable membrane. Osmosis refers to the movement of water molecules only. It is a special type of diffusion.
It is passive transport which means it does not require energy to be applied.
A dilute solution contains a high concentration of water molecules, while a concentrated solution contains a low concentration of water molecules.
The different concentrations of solutes on the two sides of the membrane cause osmotic pressure. When osmosis happens, water moves from the side of the membrane with a lower amount of osmotic pressure to the side of the membrane with the higher amount of osmotic pressure.
When the concentration of water is the same on both sides of the membrane, the movement of water molecular will be the same in both directions. There will be no net movement of water molecules.
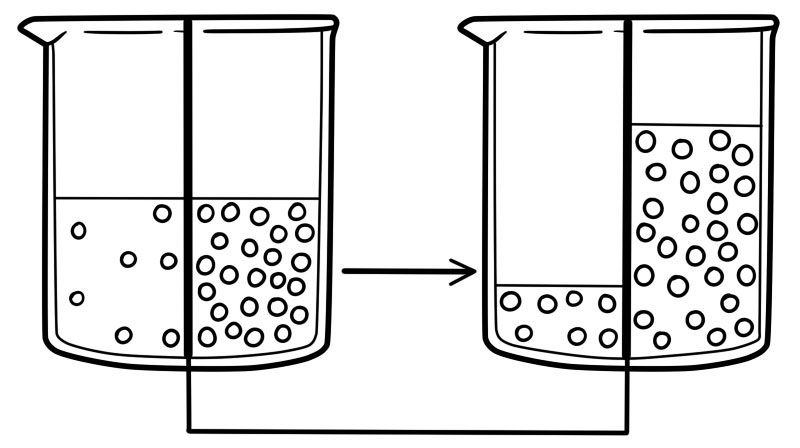
Osmosis across living cells
Cells contain dilute solutions of ions, sugars, and amino acids.
The cell membrane is partially permeable. Water will move into and out of cells by osmosis.
An important example of osmosis is the movement of liquid (solvent) molecules across a cell membrane into a cell with a higher solute concentration.
What is osmotic pressure?
Osmotic pressure is the pressure that causes the diffusion of water through semi-permeable membranes. It increases due to an increase in the concentration of solutes in the solution.
What are solvents and solutes?
Osmosis deals with chemical solutions. Solutions have two parts – a solvent, and a solute.
When a solute dissolves in a solvent, the end product is called a solution. Saltwater is an example of a solution; salt is the solute, and water is the solvent.
What are the different types of solutions?
There are three types of osmosis solutions – the isotonic solution, hypotonic solution, and hypertonic solution. Different types of solutions have different impacts on cells due to osmosis.
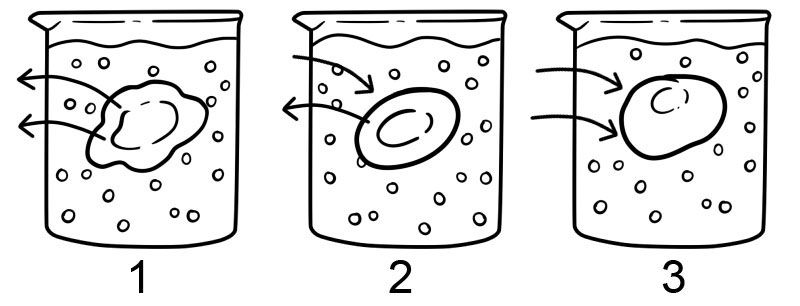
1. Hypertonic – A hypertonic solution is the opposite of a hypotonic solution; there is more solute outside the cell than inside it. In this type of solution, the water moves out of the cell and causes the cell to shrivel.
2. Isotonic – An isotonic solution has the same concentration of solutes both inside and outside the cell. Under these conditions, there is no net movement of solvent; in this case, the amount of water entering and exiting the cell’s membrane is equal.
3. Hypotonic – In a hypotonic solution, there is a higher concentration of solutes inside the cell than outside the cell. In a hypotonic solution, the water moves into the cell and can cause the cell to swell; cells that don’t have a cell wall, such as animal cells could explode in this type of solution.
Effects of osmosis in plant cells
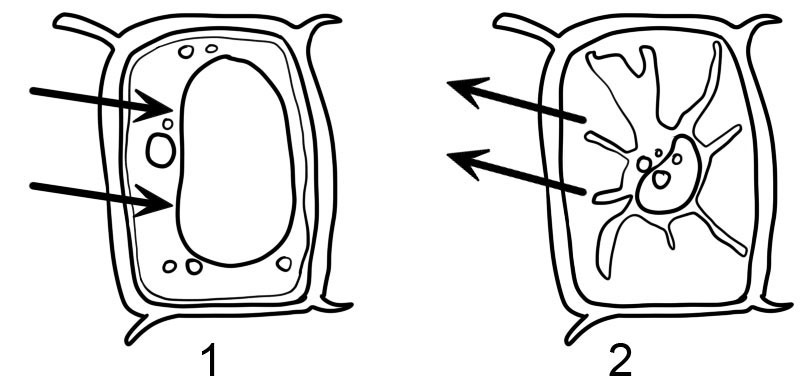
- Hypotonic
- Hypertonic
- Plant cells are enclosed by a rigid cell wall. When the plant cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, it takes up water by osmosis and starts to swell, but the cell wall prevents it from bursting. The plant cell is said to have become ‘turgid’ i.e. swollen and hard. The pressure inside the cell rises until this internal pressure is equal to the pressure outside. This liquid or hydrostatic pressure is called ‘turgor pressure’ and it prevents the further net intake of water.
- Turgidity is very important to plants as it helps with the maintenance of rigidity and stability of plant tissue, and as each cell exerts a turgor pressure on its neighbor, it creates plant tissue tension which allows the green parts of the plant to ‘stand up’ into the sunlight.
- When a plant cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, the water from inside the cell’s cytoplasm diffuse out and the plant cell is said to have become ‘flaccid’. If the plant cell is then observed under a microscope, it will be noticed that the cytoplasm has shrunk and pulled away from the cell wall. This phenomenon is called plasmolysis. The process is reversed as soon as the cells are transferred into a hypotonic solution (deplasmolysis).
- When a plant cell is placed in an isotonic solution, a phenomenon called “incipient plasmolysis’ is said to occur. ‘Incipient’ means ‘about to be’. Although the cell is not plasmoslysed, it is not turgid either. When this happens, the green parts of the plant droop and are unable to hold the leaves up in the sunlight.
Effects of osmosis in animal cells
- Animal cells do not have cell walls so, in hypotonic solutions, animal cells swell up and explode. If too much water enters the animal cell it can burst – this is called lysis. They cannot become turgid because there is no cell wall to prevent the cell from bursting. When the cell is in danger of bursting, organelles called contractile vacuoles will pump water out of the cell to prevent this from happening.
- In hypertonic solutions, water diffuses out of the cell due to osmosis and the cell shrinks. If too much water leaves the animal cell, it can shrink – this is called crenation. Thus, the animal cell always has to be surrounded by an isotonic solution. In the human body, the kidneys provide the necessary regulatory mechanism for the blood plasma. The concentration of water and salt removed from the blood by the kidneys is controlled by a part of the brain called the hypothalamus. The process of regulating the concentration of water and mineral salts in the blood is called osmoregulation.
- Animals that live on dry land must conserve water, as do animals that live in salty seawater. Animals that live in freshwater have the opposite problem; they must get rid of excess water as fast as it enters into their bodies by osmosis.


