In this lesson, you will learn
Cell division is the process in which one cell called the parent cell divides to form two new cells referred to as daughter cells. Depending on the type of organism, there are several types of cell division.
There are three main types of cell division: binary fission, mitosis, and meiosis. Binary fission is used by simple organisms like bacteria. More complex organisms gain new cells by either mitosis or meiosis.
Binary fission
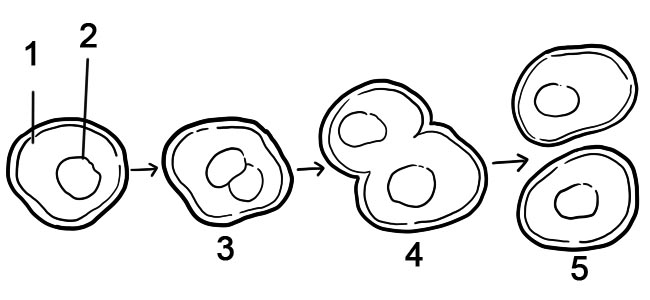
Most prokaryotic cells divide by the process of binary fission. Binary fission can be described as a series of steps, although it is actually a continuous process. The steps include DNA replication, chromosome segregation, and finally the separation into two daughter cells.
Cell division is more complex in eukaryotes than prokaryotes. Prior to dividing, all the DNA in a eukaryotic cell’s multiple chromosomes is replicated. Its organelles are also duplicated. Then, when the cell divides, it occurs in two major steps:
Mitosis
Mitosis is used when a cell needs to be replicated into exact copies of itself. Everything in the cell is duplicated. The two new cells have the same DNA, functions and genetic code. The original cell is called the mother cell and the two new cells are called daughter cells.
Examples of cells that are produced through mitosis include cells in the human body for the skin, blood, and muscles.
Cell cycle for mitosis
Cells go through different phases called the cell cycle. The “normal” state of a cell is called the interphase. The genetic material is duplicated during the interphase stage of the cell. When a cell gets the signal that it is to duplicate, it will enter the first stage of mitosis called the prophase.
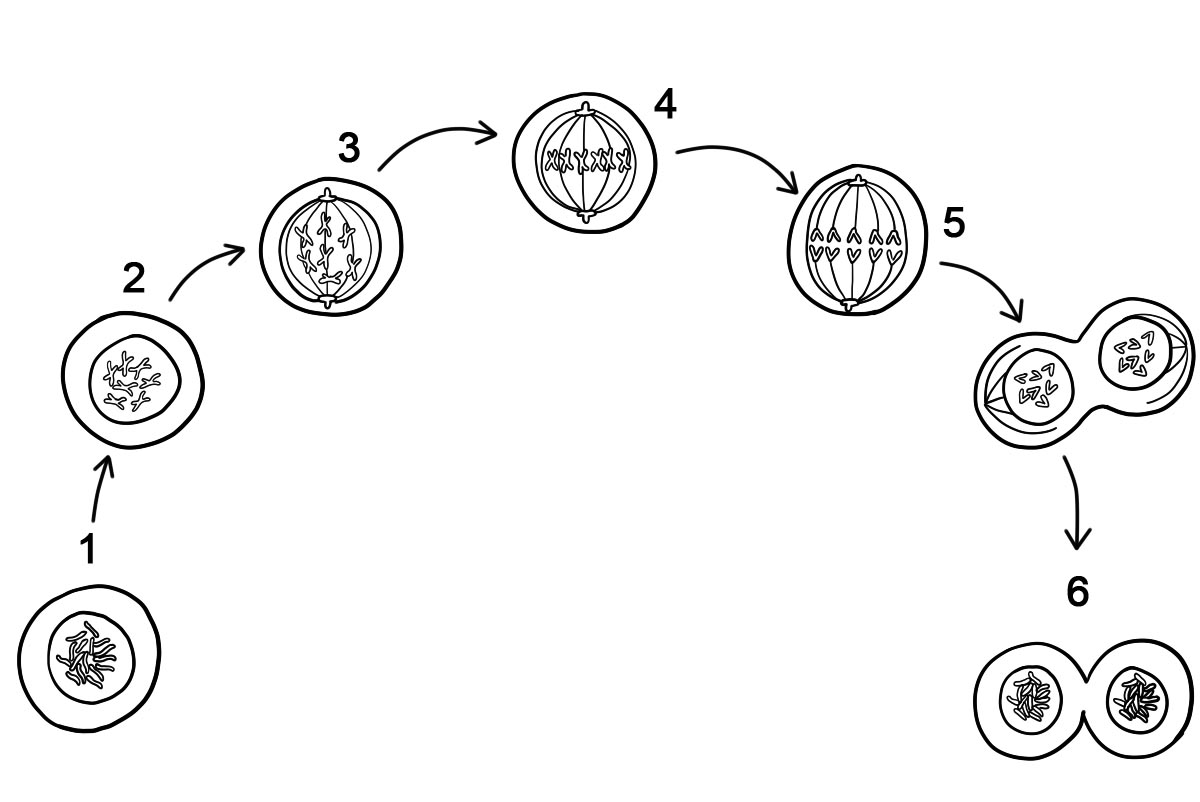
Mitosis starts with prophase in which the chromosome is condensed. The cell proceeds to metaphase where the chromosomes are aligned on the metaphase plate. Then the chromosomes are separated in anaphase and the cell’s cytoplasm is pinched apart during telophase. Cytokinesis is the final process that breaks the cell membrane and divides the cell into two.
Interphase is the normal state of a cell. It may also be known as the resting state. This is when the cell is making sure it has all the nutrients and energy to survive. It is getting ready for another division – duplicating its nucleic acids so when it’s time for prophase it has everything.
Meiosis
When it is time for the entire organism to reproduce, meiosis is used. There are two main differences between mitosis and meiosis. First, the meiosis process has two divisions. When meiosis is complete, a single cell produces four new cells instead of just two. The second difference is that the new cells only have half the DNA of the original cell. This is important for life on Earth as it allows for new genetic combinations to occur which produces variety in life.
Examples of cells that undergo meiosis include cells used in sexual reproduction called gametes.
The cells produced from mitosis are called diploids because they have two complete sets of chromosomes.
The cells produced from meiosis are called haploids because they only have half the number of chromosomes as the original cell.