In the physical world, one of the most common phenomena is motion. The branch of science which deals with the behavior of moving objects is known as ‘mechanics’.
Mechanics is further divided into two sections – Kinematics and Dynamics.
Kinematics deals with the study of motion without taking into account the cause of motion.
Dynamics is concerned with the cause of motion, namely force.
Motion means movement. An object is said to be in motion if it changes its position with respect to its surroundings in a given time. An object is said to be at rest if it does not change its position with respect to its surroundings. A frame of reference is another object or scene with respect to which we compare the position of the given object.
Each type of motion is controlled by a different type of force.
When an object covers equal distances in equal intervals of time, it is said to be in uniform motion. Uniform motion is motion at a constant speed in a straight line. Example: a rolling ball.
When an object covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time, it is said to be in non-uniform motion.
Irregular motion is motion which has no obvious pattern to its movement. Example: a flying bee.
There are two types of basic motion: translation and rotation.
Translation means motion along a path.
Rotation means motion around a fixed axis. An axis is a center around which something rotates.
Translation motion is defined by the net force (sum of different forces) acting on an object.
Rotation is defined by torque. Torque is a force which causes the rotation of an object.
Types of motion
2. Rotational motion is the movement of an object, in a circular path along a fixed point as the appointed center and the movement is along the circumference of the path, at a regular distance from the center. This type of motion is the starting point of many mechanisms. Example: a spinning wheel.
3. Reciprocating motion is back and forth motion. Example: the up and down motion of a yo-yo.

4. Oscillating motion is a reciprocating motion with elements of rotational motion like swinging. Oscillation can be a periodic motion that repeats itself in a regular cycle or equal intervals of time, like a rocking chair or the oscillation of pendulum in a clock. A pendulum which swings from a fixed point of attachment and traces an arc is a classic example of oscillating motion. A sprinkler or oscillating fan does the same thing, except that these oscillate in a horizontal plane rather than a vertical plane and are powered by motors rather than gravity. An oscillating movement is around an equilibrium point or a mean value.
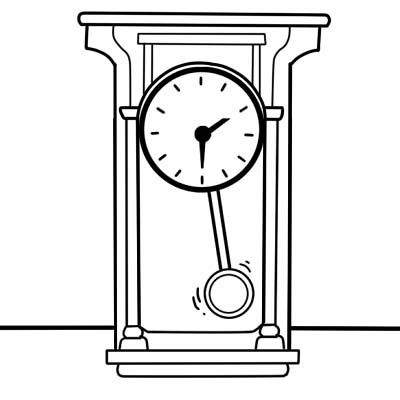
There are three variables of oscillation:
Very often, objects move by complicated motion. Complicated motion can be broken down into simpler types of motion. An example of complicated motion is a flying Frisbee. The movement of a Frisbee consists of linear motion and rotary motion.
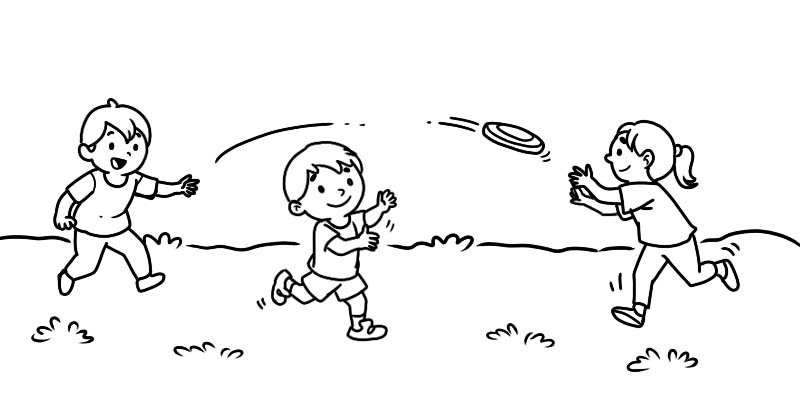

Frictional and gravitational forces affect the motion of objects – they slow down the motion.
The frictional force which slows a body in motion, and eventually stops a moving object is called kinetic friction. For example, when you push a box across the floor, part of the energy of your pushing moves the box, and part of the energy is lost to kinetic friction. The less textured the surface, the farther the object will move. This happens because smooth surfaces have less frictional force. Friction is affected by the texture of both the surface and the moving object.
Distance and Displacement
The distance between terminus A and terminus B is 150 km. A bus travels from terminus A to terminus B. The distance covered by the bus is 150 km. While traveling on the same route, the bus returns from terminus B to the terminus A. Thus the total distance covered by the bus during the trip from A to B and then from B to A is 150 km + 150 km = 300 km.
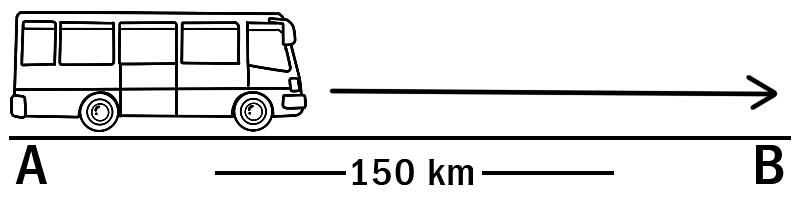
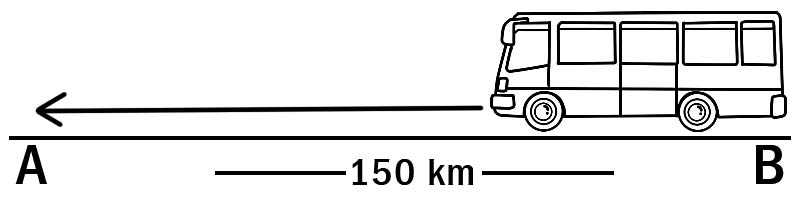
A bus moving from A to B and again from B to A
What is inertia?
Inertia means resistance to any change in motion. All objects have inertia. The larger the mass of an object, the more inertia it has. Newton’s First Law of Motion states that moving objects will continue moving in the same direction and at the same speed. It also states that objects at rest unless an outside force acts on them. When the driver of a car puts on the brakes, the car slows down. The people in the car, however, will continue at the same speed the car was going because of their inertia. The seatbelt acts as a force to keep the people in place. Seatbelts help keep people from getting hurt when a car comes to a sudden stop.
Simple Harmonic Motion
Simple harmonic motion (SHM) is a type of oscillatory motion. A simple harmonic motion has three things, it basically does: Motion always goes back to equilibrium, follows the same path and oscillates around the equilibrium. SHM results when the force or torque that tends to restore equilibrium is directly proportional to the displacement from the equilibrium are directly proportional to the displacement from equilibrium.
Speed is the distance covered in a given time. Speed = Distance/Time. SI unit of speed is m/s. Speed is a scalar quantity.
An object is moving with uniform speed if it covers equal distances in equal intervals of time.
If the distance covered varies with time, the object is said to be moving with variable speed.
Average speed and Instantaneous speed
When we travel in a vehicle the speed of the vehicle changes from time to time, depending upon the conditions existing on the road. In such a situation, the speed is calculated by taking the ratio of the total distance traveled by the vehicle to the total time taken for the journey. This is called the average speed.
Instantaneous speed would be the speed at any given instant within that span of time, measured with a real-time speedometer.
Velocity
Velocity is defined as the distance covered by a moving object in a particular direction in unit time or speed in a particular direction.
Velocity = (distance traveled in a specified direction)/time taken
Velocity can also be defined as the rate of change of displacement.
Velocity is a vector quantity.
A body is said to be moving with uniform velocity if it covers equal distances in equal intervals of time in a specified direction.
A body is said to be moving with variable velocity if it uncovers unequal distances in equal intervals of time and vice versa in a specified direction or if it changes the direction of motion.
Acceleration
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity of a moving body with time. This change could be a change in the speed of the object or its direction of motion or both.
Acceleration = Rate of change of velocity with time
SI unit of acceleration is m/s2
Acceleration is a vector quantity.
There are different types of acceleration: