You will learn:
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are chemically joined together. For example, two atoms of hydrogen combine to form a molecule of hydrogen. Similarly, one atom of sodium combines with one atom of chlorine to form a molecule of sodium chloride. We can also say, a molecule is the smallest particle of an element or a compound that is capable of independent existence and shows all properties of that element or compound.
We can divide molecules into molecules of elements and molecules of compounds.
Molecules of an element are made of the same type of atoms. Molecules of some elements such as helium (He) are made of only one atom of that element. But atoms of elements like oxygen, nitrogen, etc. cannot exist independently.
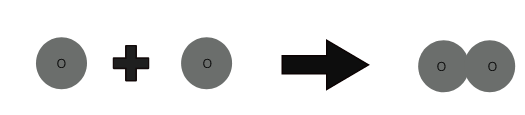
1 oxygen atom + 1 oxygen atom ⇒ 1 oxygen molecule
The number of atoms present in a molecule of an element is called its atomicity. Atomicity can be monoatomic, diatomic, triatomic and polyatomic.
| Atomicity | Number of atoms | Examples |
| Monoatomic | 1 | Noble gases such as Helium(\(He\)), Neon(\(Ne\)) |
| Diatomic | 2 |
Hydrogen(\(H_2\)) Chlorine(\(Cl_2\)) |
| Triatomic | 3 | Ozone(\(O_3\)) |
| Polyatomic | > 2 |
Phosphorus(\(P_4\)) Atomicity 4 Sulfur(\(S_8\)) Atomicity 8 |
A chemical compound refers to a chemical substance that is composed of many identical molecules that are composed of atoms from more than one element joined together by chemical bonds. Two atoms from the same element bonded in a molecule do not form a chemical compound, this is because this requires two different elements.
Most substances found in nature – such as wood, soil, and rocks – are mixtures of chemical compounds.
A defining characteristic of a compound is that it has a chemical formula. Formulas describe the ratio of atoms in a substance. For example, the formula of a water molecule is H2O. this indicates that two hydrogen atoms are bonded to one oxygen atom.
Atoms of different elements combine together in a definite proportion to form molecules of compounds. For example, water (\(H_2O\)) represents a molecule of the compound water in which two atoms of hydrogen combine with one atom of oxygen.
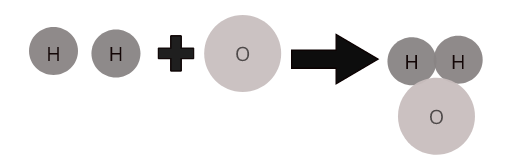
Molecules of some common compounds:
| Compound | Combining elements |
| Hydrogen chloride (\(HCl\)) | Hydrogen, Chlorine |
| Water (\(H_2O\)) | Hydrogen, Oxygen |
| Carbon dioxide (\(CO_2\)) | Carbon, Oxygen |
When atoms come closer to each other, they combine to form molecules. When they combine, one atom gives or donates one or more electrons which is accepted by the other atoms. As a result, a chemical bond is formed which holds atoms together to form a compound.
Valency is the number of electrons that an atom can denote or accept to form a chemical compound or molecules with another atom. It is the combining capacity of an atom of an element.
A valency is always a whole number. Elements with valency 1 are called monovalent. Elements with valency 2 are called divalent and valency equal to 3 are called trivalent. Many elements have variable valency (more than one valency). An element with more than one valency is written as the name of the element followed by a Roman numeral in the brackets to indicate the valency. For example, copper with valency 1 is written as Copper[I]
Few elements and their valency:
| Element | Valency |
| Hydrogen (\(H\)) | 1 |
| Helium(\(He\)) | 0 |
| Carbon(\(C\)) | 4 |
| Nitrogen(\(N\)) | 3 |
| Oxygen(\(O\)) | 2 |
| Sodium(\(Na\)) | 1 |
| Magnesium(\(Mg\)) | 2 |
| Phosphorus(\(P\)) | 3 |
| Sulfur(\(S\)) | 2 |
| Chlorine(\(Cl\)) | 1 |
| Potassium(\(K\)) | 1 |
| Calcium(\(Ca\)) | 2 |
| Copper(\(Cu\)) |
1 2 |
| Iron(\(Fe\)) |
2 3 |
The chemical formula of a compound is the symbolic representation of its composition. It tells us the number of atoms of various elements present in one molecule of a compound.
Rules for writing the formula of a compound:
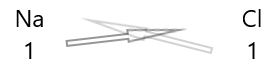
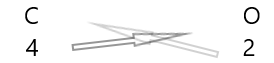
1. Write the symbol of the elements and their valency below them.
2. Interchange their valency and write them as subscripts.
3. If valencies in the chemical formula are divisible by any factor, divide and simplify.
Chemical compounds show a bewildering array of characteristics. At ordinary temperatures and pressures, some are solids, some are liquids and some are gases. The chemical compounds are of varied colors. Some compounds are highly toxic to humans, whereas others are essential for life. The substitution of only a single atom within a compound may be responsible for changing the color, odor, or toxicity of a substance.