All matter is made up of atoms and molecules. As atoms are the smallest units of matter, molecules are composed of two or more atoms.
In this lesson, we are going to discuss the molecules found in living organisms, called biomolecules. We will learn:
Molecules that are found in living organisms are called biomolecules. They are also called biological molecules. Biomolecules are any of numerous substances that are produced by cells and living organisms. They have a wide range of sizes and structures and perform a vast array of functions, as well. Each is an important component of the cell. Combined, these molecules make up the majority of a cell's mass. They are the building blocks of life.
Biomolecules consist mainly of carbon and hydrogen with nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, and phosphorus.
Biomolecules include large macromolecules, such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids, as well as small molecules such as primary metabolites, secondary metabolites, and natural products (any substance produced by life).
A primary metabolite is a kind of metabolite that is directly involved in normal growth, development, and reproduction. It usually performs a physiological function in the organism, and some examples of them include certain amino acids.
Secondary metabolites are also called specialized metabolites, secondary products, toxins, or natural products. They are organic compounds. They do not play a role in growth, development, and reproduction like primary metabolites do.
Macromolecules are large, complex molecules, composed of thousands of atoms. All life is composed mainly of the four macromolecule building blocks: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. All four of those types of biomolecules contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
Like all other macromolecules, carbohydrates are built from smaller organic molecules and are necessary for life. Their name comes from the composition. Because they are made up of carbon and water (hydro), they are called carbohydrates. Living organisms use carbohydrates as accessible energy to fuel cellular reactions and for structural support inside cell walls. They provide our bodies with energy, particularly through glucose. Glucose is a simple sugar that is a component of starch and an ingredient in many basic foods. Sugar is a source of quick energy for the body because it is easily metabolized (broken down). Carbohydrates can be divided into groups according to the number of individual simple sugar units. Monosaccharides contain a single sugar unit; disaccharides contain two sugar units, and polysaccharides contain many sugar units as in polymers - most contain glucose as the monosaccharide unit.
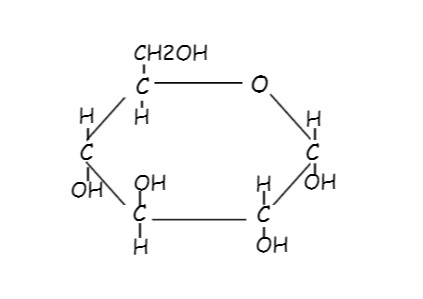
Chemical structure of Glucose, which is a simple sugar
Lipids are a diverse group of hydrophobic (“water-fearing”), or insoluble in water bio-molecules. But, lipids are smaller than the other three types of macromolecules, and the main difference with them is that the lipids do not form polymers. So, we will conclude that lipids are not polymers, because they are not built from monomers. They are long chains of carbon and hydrogen molecules and are classified as simple and complex. Major types include fats and oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. Lipids perform different functions in cells. They are responsible for storing energy, signaling, and they are acting as structural components of cell membranes. The most common form of lipid found in food is triglycerides. Triglycerides contain a glycerol molecule and 3 fatty acids. Lipids provide insulation in our bodies to keep us warm.
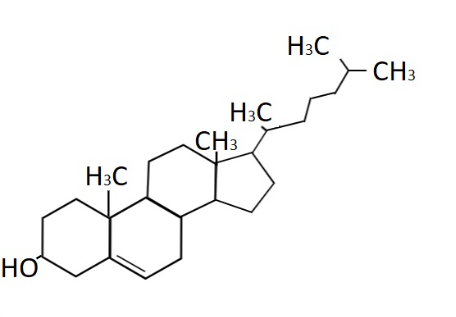
Chemical structure of Cholesterol, a type of Lipid
Proteins are biomolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. There are 20 different types of amino acids that can be combined to make a protein. Proteins play many critical roles in the body. They do most of the work in cells. Also, the proteins are required for the function, structure, and regulation of the body’s organs and tissues. Protein is an important building block of bones, muscles, cartilage, skin, and blood. Hair and nails are mostly made of protein. Protein provides the body with approximately 10 to 15% of its dietary energy. It is the second most abundant compound in the body, following water.
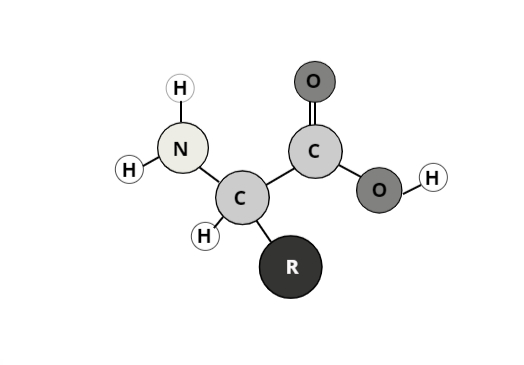
Chemical structure of Amino acid
Nucleic acids are the biological macromolecules essential to all known forms of life. The term nucleic acid is the overall name for DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (Ribonucleic acid). They are composed of nucleotides. A nucleotide is made up of three components: a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. The functions of nucleic acids have to do with the storage and expression of genetic information, they code the genetic information of organisms.

DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
Biomolecules also include: